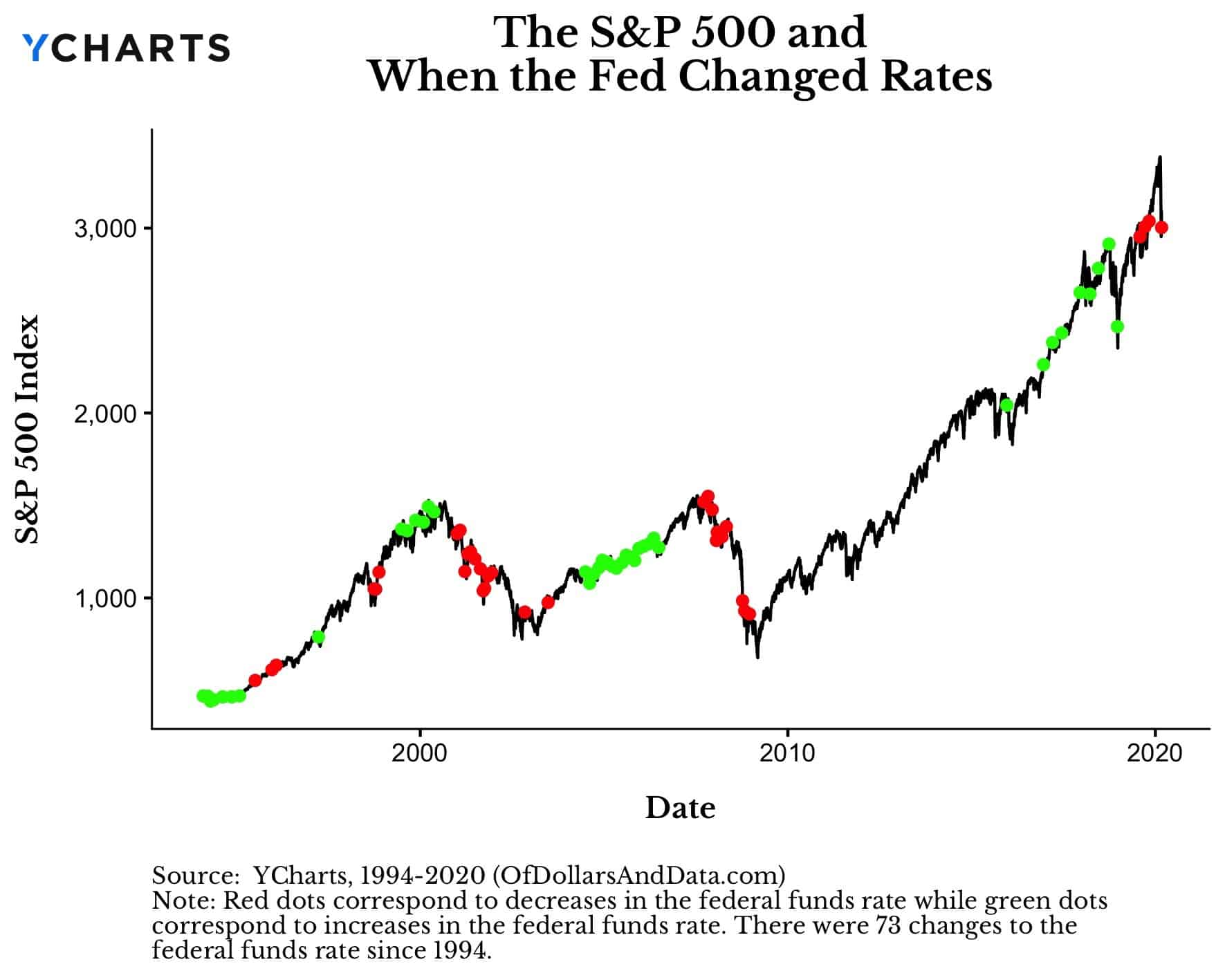
The recent Fed rate cut effects are beginning to ripple across the economy, bringing both hope and uncertainty to consumers and businesses alike. As the Federal Reserve lowers borrowing costs for the first time in four years, many are looking eagerly to how these changes might influence interest rates impact on mortgages, credit cards, and overall consumer spending. Economists predict that mortgage rate changes will likely trend downwards as the Fed continues its easing policy, which could provide much-needed consumer debt relief amidst rising economic pressures. In addition, these lower rates are expected to boost housing affordability, making it easier for potential homebuyers to enter the market. While economic growth predictions remain cautious, the implications of this rate cut could indeed signal a more favorable landscape for both Wall Street and Main Street, if managed effectively.
The implications of the Federal Reserve’s recent decision to reduce interest rates are multifaceted and could play a critical role in shaping financial markets and consumer behavior. This move may be seen as a key strategy to stimulate economic activity and curb the rising costs associated with borrowing. Particularly for individuals facing significant personal loans, such as mortgages, this adjustment could alleviate some financial burdens and enhance overall affordability in the housing market. As we delve into the intricate relationship between interest rates and economic stability, it’s crucial to explore how these reductions can foster a healthier environment for economic growth and consumer confidence moving forward. Understanding these dynamics not only informs stakeholders but also prepares them for the possible outcomes that might emerge in the wake of such monetary policy changes.
Understanding the Impacts of the Fed Rate Cut
The recent Federal Reserve rate cut has captured the attention of both economists and consumers alike, primarily because its ramifications can reshape financial landscapes. By lowering interest rates, the Fed anticipates a boost in borrowing and spending, which could spurt economic growth and revive sectors like housing and consumer goods. However, it is important to understand that while the initial cut may seem beneficial, the actual impacts on various sectors will unfold gradually over time, requiring close monitoring from both market participants and consumers.
For homebuyers, the Fed rate cut symbolizes potential relief from escalating mortgage rates, making housing more affordable and accessible. As rates decrease, many first-time buyers might feel encouraged to enter the housing market. However, the lingering question remains regarding how quickly these benefits ripple through the economy. As economic growth predictions fluctuate, the actual realization of cheaper loans and enhanced consumer confidence hinges on broader economic indicators as well as individual financial situations.
The Relation Between Fed Rate Cuts and Mortgage Rate Changes
When the Federal Reserve cuts rates, it is often interpreted as a direct pathway to lower mortgage rates. Typically, a cut in the federal funds rate leads to decreased costs for banks which, in theory, should translate into lower rates for consumers looking to secure home loans. As highlighted by economist Jason Furman, ongoing reductions in mortgage rates could significantly address the housing affordability crisis many regions face, thereby providing much-needed support for potential homeowners.
However, it is crucial to note that the relationship between Fed rate cuts and mortgage rates is not always linear. Other factors such as inflation, bond yields, and economic recovery play influential roles in determining mortgage rate changes. Although consumers are likely to see some relief in terms of housing affordability, experts caution that additional factors will affect how quickly and efficiently these rate cuts are absorbed into the mortgage market.
Consumer Debt Relief Following Rate Cuts
Consumer debt is an ever-pressing issue in today’s economy, dominated by high credit card balances and loans. The latest Fed rate cut has generated discussions about possible relief for consumers struggling with debt. Lowering rates could alleviate the burden slightly by reducing monthly payments on variable-rate loans. However, while consumers might benefit in the long run, short-term relief may still be limited due to persistent high-interest rates across various debts.
The expectation that consumers can swiftly return to pre-pandemic debt levels may be overly optimistic. With debt repayment behaviors showing gradual improvement, coupled with the anticipated tightening of lending standards, many will find it challenging to take full advantage of the rates drop. As the economy slowly shifts, consumers should remain vigilant about managing their debts and seek strategies to maximize the benefits arising from the Fed’s proactive monetary policies.
Economic Growth Predictions Post Fed Rate Cuts
Following the recent decision to cut rates, many economists are reevaluating their growth predictions for the upcoming year. The intent behind such cuts is to stimulate economic activity, and as interest rates become more favorable, business investments and consumer spending are likely to experience a boost. The ripple effect of this increased spending could potentially lead to job creation and an improved labor market, reflecting a positive prognosis for overall economic growth.
However, uncertainty lingers over how soon these growth predictions will manifest amid unstable inflation rates and global economic influences. While the Fed’s intention is to balance economic recovery with manageable inflation, the effectiveness of such measures will largely depend on market receptivity and consumer confidence, which need to be nurtured over time for lasting dividends to emerge.
The Role of Consumer Confidence in Economic Recovery
Consumer confidence plays a pivotal role in the trajectory of economic recovery following Fed rate changes. When consumers feel secure in their financial situation, they are more likely to increase spending, which in turn fuels economic growth. The Fed’s proactive stance regarding interest rates aims to bolster this confidence, making it vital for stakeholders to observe fluctuations in consumer sentiment closely.
Moreover, as credit becomes cheaper through rate cuts, individuals may feel more inclined to take larger financial risks, potentially leading to investments in business or home purchases. It’s essential for both policymakers and business leaders to understand how consumer confidence interacts with economic changes resulting from rate cuts, as a lack of confidence can negate the positive impacts intended by monetary policy adjustments.
Long-term Housing Affordability After Fed Rate Cut
Housing affordability has become a pressing concern, particularly for millennials and first-time buyers. Although the recent Fed rate cuts might ease some burdens by making mortgage loans cheaper, the long-term implications on housing affordability are complex and multifaceted. As the market reacts to these changes, it is important to recognize that other economic factors, such as supply shortages and inflationary pressures, will continue to influence home prices, possibly offsetting gains from lower mortgage rates.
As economists predict a gradual decline in mortgage rates over time, it remains crucial for potential homebuyers to remain informed about the housing market’s fluctuations. Increased purchasing power, paired with a potential easing of housing supply constraints, could create a window of opportunity for buyers. Nevertheless, those hoping for quick resolutions to longstanding affordability issues may need to apply more patience as the economy adjusts to the outcomes of recent rate cuts.
Exploring the Side Effects of Rate Cuts on Inflation
While rate cuts are often hailed as tools to stimulate economic growth, they can inadvertently intensify inflationary pressures. As borrowing becomes cheaper, increased consumer spending can push demand beyond supply capabilities, leading to price hikes. Therefore, it’s imperative to consider how sustained low-interest environments may not inherently equate to economic stability, as they can lead to volatility in inflation rates.
Moreover, the Federal Reserve’s challenge lies in finding a balance between stimulating growth and keeping inflation in check. Policymakers must remain vigilant about the potential for overheating the economy, especially if rate cuts lead to enhanced consumer confidence and spending sprees that outpace production. This delicate balancing act will be critical in managing long-term economic health.
Impacts of Rate Cuts on Different Economic Sectors
The implications of the recent Fed rate cut extend beyond just consumer borrowing; various economic sectors will experience different degrees of impact. Industries such as real estate and retail may see immediate benefits from reduced borrowing costs, while others like finance could face challenges due to interest rate spread compression which may squeeze profit margins. Understanding these sector-specific effects is essential for investors and policymakers targeted with tailoring interventions.
Additionally, sectors reliant on consumer discretionary spending may benefit the most from enhanced financial conditions, as lower rates can inspire increased purchasing activity. On the other hand, sectors like manufacturing may not react as rapidly, given that their larger investments often rely on different financial dynamics. Thus, a comprehensive understanding of how rate cuts affect individual sectors is essential in navigating the evolving economic landscape.
Consumer Expectations in a Lower Interest Rate Environment
With the Fed’s recent move to cut interest rates, consumer expectations are beginning to adjust to a potentially long-term lower-interest environment. As borrowing becomes more accessible, individuals may start to reevaluate their financial strategies, often considering making larger purchases, investing, or even consolidating debt. Adjusting expectations around interest costs reflects a significant shift in consumer behavior that can significantly influence economic activity.
However, consumers should remain cautious about overextending themselves. While the allure of lower rates is tempting, it is essential to maintain a sustainable approach to personal financing and budgeting. As the economic environment evolves, staying informed about potential changes will empower consumers to make choices that align with both their short-term needs and long-term financial goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the Fed rate cut effects on interest rates and consumer loans?
The Fed rate cut effects on interest rates lead to a decrease in the cost of borrowing, making loans like credit cards, auto loans, and mortgages cheaper for consumers. As the Federal Reserve lowers rates, banks typically follow by reducing their interest rates, which can provide relief to consumers managing debt.
How will the Fed rate cut affect mortgage rates and housing affordability?
The Fed rate cut is likely to drive mortgage rates down, improving housing affordability. While recent cuts have already led to lower mortgage rates, continued easing by the Fed is expected to further enhance affordability for homebuyers, thereby impacting the overall housing market positively.
What are the implications of Fed rate cuts for economic growth predictions?
Fed rate cuts generally stimulate economic growth by encouraging spending and investment due to lower borrowing costs. With cheaper loans, consumers and businesses are more likely to spend, which can lead to job creation and economic expansion over the horizon of six to twelve months.
Will consumers see debt relief following the Fed rate cuts?
Yes, consumers can expect some debt relief in the longer term due to the Fed rate cuts. As borrowing costs decrease, those with high-interest debts like credit cards may see their interest rates decline, although significant immediate relief might not occur for several months.
How do Fed rate cuts impact overall consumer confidence and spending?
The Fed rate cuts can boost consumer confidence and spending by signaling an accommodative monetary policy aimed at stimulating the economy. When consumers perceive lower borrowing costs and favorable conditions, they are more inclined to spend, which is vital for economic health.
What influence do Fed rate cuts have on inflation and economic stability?
Fed rate cuts can lead to moderate inflation increases as lower rates usually boost spending and investment. However, by proactively managing interest rates, the Fed aims to prevent overheating in the economy and maintain stability while supporting growth.
When can we expect to see the full effects of the recent Fed rate cuts?
The full effects of the recent Fed rate cuts may take 6 to 12 months to manifest fully in the economy. While immediate changes can be seen in borrowing costs, the broader impacts on job creation and economic growth will unfold over time.
Are there risks associated with further Fed rate cuts?
Yes, while Fed rate cuts aim to stimulate growth, they also carry risks such as potential overheating of the economy and problems like rising inflation. The Fed must carefully balance cuts to avoid destabilizing the economy or creating asset bubbles.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Fed Rate Cut | The Fed cut interest rates by 0.5%, the first reduction in four years, to lower borrowing costs. |
| Impact on Consumers | Consumers can expect benefits, particularly with credit card debt and mortgages, but the timeline is uncertain. |
| Market Predictions | Economists predict potential further cuts by the Fed, with expectations of two more 0.25% reductions this year. |
| Mortgage Rates | Mortgage rates are likely to decrease further as the Fed continues to ease policy, slightly helping housing affordability. |
| Business Impact | Immediate business impact may be minimal, but gradual economic growth and job creation are expected over the next 6-12 months. |
Summary
The Fed rate cut effects are expected to create a ripple of positive outcomes for consumers and the economy at large. While the immediate benefits of lower interest rates are welcomed, the full impact on borrowing costs, housing affordability, and economic growth will manifest over time. With further cuts anticipated, consumers holding debt may find relief, although some uncertainty remains regarding how quickly rates will drop and the extent of these benefits.