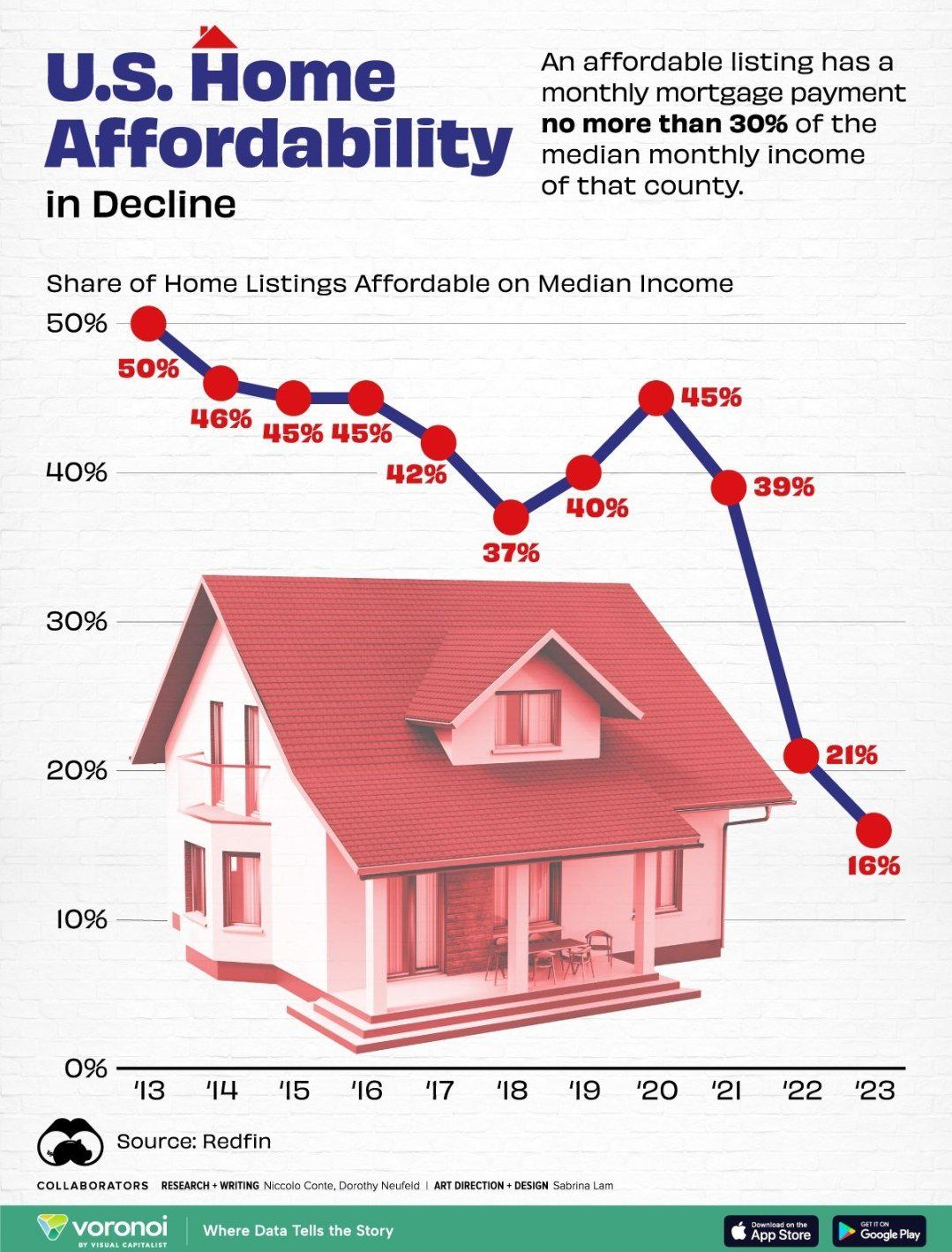
The United States is grappling with a housing affordability crisis that has rendered homeownership unattainable for many Americans. As housing market trends indicate soaring prices, factors such as labor costs, material expenses, and the impact of NIMBY policies play critical roles in this ongoing dilemma. A significant reason for the inflated costs is attributed to restrictive land-use regulations that hinder construction productivity, preventing builders from delivering homes at scale. Over the past few decades, homeownership challenges have intensified, highlighting the urgent need for reforms that enhance housing access and affordability. Addressing these interconnected issues is essential not only for potential homeowners but also for the economic stability of communities nationwide.
America is experiencing a severe crisis in housing affordability, with many individuals finding it increasingly difficult to achieve homeownership. This predicament arises within the broader context of housing market dynamics, influenced by restrictive local policies and land-use regulations that disproportionately burden new construction. Compounding these challenges is the declining productivity in the construction sector, which has struggled to meet the rising demand for affordable housing. As more families encounter barriers to securing a stable living situation, understanding the intersection of market trends and regulatory frameworks becomes vital. A thoughtful examination of these elements can inform targeted solutions aimed at alleviating the strain on housing availability.
Understanding the Housing Affordability Crisis
The housing affordability crisis is a pressing issue in the United States, stemming from rising prices and stagnant wages. As new single-family homes have doubled in price since 1960, many Americans find homeownership increasingly unattainable. The crisis is exacerbated by limited housing options, resulting from restrictive land-use regulations and construction challenges that prevent the development of affordable housing. LSI keywords such as ‘housing market trends’ and ‘homeownership challenges’ highlight the factors contributing to this growing issue.
The ongoing affordability crisis has far-reaching consequences, affecting not just potential homeowners but also the overall economy. High housing costs limit consumer spending power and prevent the workforce from fully participating in the job market. As prices continue to climb, younger generations find themselves unable to invest in homes, leading to lower rates of homeownership which can stifle economic growth. A comprehensive understanding of the crisis involves examining how ‘NIMBY’ policies and construction productivity issues hinder the development of adequate housing solutions.
The Impact of NIMBY Policies on Housing Development
Not In My Backyard (NIMBY) policies have become a significant barrier to expanding the housing supply. These regulations often empower local communities to resist new construction projects, perpetuating low-density, single-family home developments instead of fostering diverse and affordable housing options. As more people push back against developments, the resulting stagnation leads to higher home prices and exacerbates the affordability crisis. The relationship between NIMBYism and the broader housing market trends is evident, highlighting how local opposition directly impacts housing availability.
Furthermore, the restrictive nature of NIMBY policies places a considerable burden on builders. They are often forced to navigate through extensive approval processes that can delay projects for months or even years. This added layer of bureaucracy limits construction productivity and discourages innovation in housing design and manufacturing. As Edward Glaeser points out, regulations compel builders to create bespoke homes that cater to community demands, rather than allowing for scalable and efficient housing production.
Land-Use Regulations and Their Role in Housing Costs
Land-use regulations are crucial in understanding the dynamics of the housing market. These regulations dictate how land can be used, which directly influences housing supply and demand. Over the decades, land-use policies have become more stringent, significantly slowing down the pace of housing construction. It’s evident that with tighter controls, the size of housing developments has decreased, leading to smaller firms that lack the innovation capacity of larger builders. This not only reduces the number of homes being built but also raises overall construction costs.
The research by Glaeser and his colleagues underscores the correlation between land-use restrictions, construction productivity, and housing prices. By limiting the size and scope of construction projects, these regulations hinder economies of scale that are essential for lowering costs. As a result, homes are built at higher prices, making them increasingly unaffordable for the average American. This combination of rising costs and limited housing availability creates an environment where only the wealthy can comfortably invest in homeownership, marginalizing the lower and middle-income demographics.
Construction Productivity Challenges
The decline in construction productivity over recent decades presents a significant challenge to addressing the housing affordability crisis. Research has shown that since 1970, productivity in construction has stagnated, contrasting sharply with gains in other sectors such as manufacturing. Traditional approaches to homebuilding, which focus on smaller, individualized projects due to regulatory constraints, have failed to leverage mass production efficiencies. As a result, the costs associated with homebuilding remain high, further straining access to affordable housing.
In addition to lower productivity, innovation within the construction sector has waned. The decline in construction patents over the past few decades indicates a lack of technological advancement compared to other industries. This stagnation hinders the introduction of new building methods or materials that could improve efficiency and affordability. Addressing the construction productivity challenges is fundamental to revitalizing the housing market and providing sustainable solutions to the affordability crisis.
Reviving Homeownership Opportunities
Reviving homeownership opportunities requires a multi-faceted approach that addresses the entrenched issues stemming from NIMBY policies and land-use regulations. One potential solution is to advocate for policy reforms that incentivize developers to build larger-scale housing projects. By creating a more favorable regulatory environment, builders would be able to harness economies of scale, ultimately driving down costs and increasing the stock of affordable homes.
Furthermore, education and community engagement play crucial roles in overcoming resistance to new developments. By fostering understanding and collaboration among stakeholders, communities can work towards balanced solutions that allow for responsible growth while addressing local concerns. Empowering local citizens to see the benefits of increased housing availability can transform NIMBY attitudes and pave the way for innovative housing solutions that support broader economic stability.
Long-Term Implications of Housing Market Trends
The long-term implications of current housing market trends are profound, particularly if the affordability crisis continues unchecked. As wealth becomes concentrated in homeowners, younger generations may face increasingly insurmountable barriers to entry in the housing market, leading to socioeconomic divides. If trends persist, we may witness a decline in overall economic mobility, as homeownership has traditionally been a cornerstone of wealth accumulation in the United States.
Moreover, cities are at risk of becoming homogenized, catering solely to affluent demographics while neglecting the needs of lower-income families. The lack of diverse housing options diminishes community vibrancy and can exacerbate issues related to economic disparity. To combat these negative outcomes, comprehensive strategies to manage land-use regulations, improve construction productivity, and enhance the housing supply are essential in shaping a more equitable future.
Innovations in Housing Solutions
Innovation in housing solutions is vital for combating the affordability crisis. Forward-thinking approaches, such as modular and prefabricated homes, can streamline construction processes and significantly reduce costs. These methods leverage technology and manufacturing techniques to produce homes faster and more affordably, making them an attractive alternative to traditional building methods. Through the adoption of innovative housing models, we can explore new avenues for expanding homeownership opportunities.
Additionally, fostering partnerships between public entities, private developers, and community organizations can lead to pioneering housing initiatives. Collaborative efforts may facilitate the development of mixed-income projects that not only provide affordable housing but also promote social cohesion among diverse communities. Innovations in housing solutions must prioritize sustainability and accessibility, ultimately supporting a more resilient and vibrant housing landscape.
The Role of Economic Policies in Housing Affordability
Economic policies are pivotal in shaping the housing landscape. By crafting fiscal strategies that support affordable housing initiatives, lawmakers can address the supply shortages exacerbated by restrictive regulations. Targeted incentives for builders to create affordable units can elevate the construction of housing options for lower-income families, reducing the strain on the housing market. Moreover, policies that prioritize urban redevelopment can rejuvenate areas in need of revitalization, thus increasing overall housing availability.
Additionally, addressing broader economic factors, such as wage growth and job opportunities, is crucial for enhancing housing affordability. Programs aimed at increasing earnings for lower-income households can empower individuals to invest in homeownership, thus bridging the gap between income levels and housing prices. A holistic approach to economic policymaking that intertwines with housing strategies will be essential in creating a sustainable path toward improved affordability.
Collaboration Between Stakeholders for Housing Solutions
Collaboration among stakeholders is essential for addressing the complex challenges of housing affordability. Developers, policymakers, local communities, and housing advocates must come together to create comprehensive solutions that balance the needs of various interests. An inclusive dialogue can help dismantle NIMBY attitudes by encouraging understanding and openness towards new construction aimed at fostering community growth.
By forming partnerships that focus on shared goals, stakeholders can innovate and implement projects that satisfy both regulatory requirements and community aspirations. Engaging community members in the planning process empowers them to take ownership of developments, fostering a sense of pride and responsibility towards new housing projects. Such collaborations can lead to improved housing strategies that not only alleviate the affordability crisis but also enhance social cohesion in communities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the housing affordability crisis and how does it relate to housing market trends?
The housing affordability crisis refers to the significant gap between rising home prices and the income levels of many citizens, making it difficult for families to secure affordable housing. This issue is exacerbated by housing market trends that show increasing prices of homes, limited inventory, and growing demand without corresponding wage growth, effectively pushing homeownership beyond the reach of a widening segment of the population.
How do NIMBY policies impact the housing affordability crisis?
NIMBY (Not In My Backyard) policies contribute significantly to the housing affordability crisis by imposing restrictive land-use regulations that prevent new housing developments. These policies often arise from community opposition to high-density buildings or affordable housing projects, thereby limiting the supply of new homes and driving up prices, making it challenging for many to enter the housing market.
What role do land-use regulations play in the housing affordability crisis?
Land-use regulations often restrict the type, size, and scale of housing developments, causing delays and diminishing productivity in construction. Such regulations can lead to smaller housing projects, which are less efficient and result in higher overall housing costs. This regulatory burden contributes to the ongoing housing affordability crisis by reducing the supply of available homes on the market.
How does construction productivity relate to the housing affordability crisis?
Construction productivity has stagnated over the past few decades, largely due to increasing land-use regulations and smaller project sizes influenced by NIMBY attitudes. This decline in productivity means fewer homes are built per worker, leading to insufficient supply in the face of high demand, ultimately exacerbating the housing affordability crisis. Without improved construction efficiency, achieving affordable homeownership becomes increasingly difficult.
What are the homeownership challenges associated with the housing affordability crisis?
The homeownership challenges stemming from the housing affordability crisis include skyrocketing home prices that outpace wage growth, increased competition for limited housing inventory, and restrictive lending policies. Many potential buyers are unable to save for down payments or secure loans at favorable rates, leading to prolonged renting or housing instability, further entrenching the cycle of affordability issues.
How can understanding housing market trends help address the housing affordability crisis?
Understanding housing market trends is crucial for addressing the housing affordability crisis, as it provides insights into price fluctuations, inventory levels, and demographic shifts. Policymakers and stakeholders can use this information to devise strategies that enhance housing supply, balance demand, and facilitate access to affordable homeownership options, ultimately contributing to a more stable housing market.
What innovative solutions can be implemented to combat the housing affordability crisis?
Innovative solutions to combat the housing affordability crisis may include promoting modular and prefabricated housing, incentivizing adaptive reuse of existing structures, easing zoning restrictions, and implementing inclusionary zoning practices. By fostering creative approaches to construction and development, we can increase housing supply and affordability, making homeownership more attainable for many.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Housing Affordability Crisis | The U.S. is facing a significant housing affordability crisis where homeownership is increasingly out of reach for many Americans. |
| Increase in Home Prices | Since 1960, the cost of new single-family homes has more than doubled, influenced by various factors such as rising labor and material costs. |
| Impact of NIMBY Policies | “Not in my backyard” (NIMBY) land-use regulations are limiting the size and scope of housing projects, negatively impacting builders’ productivity and innovation. |
| Productivity Decline | The construction sector’s productivity has significantly decreased since 1970, despite overall economic growth, due to increased land-use regulations. |
| Historical Comparison | Large builders in the past, like those who developed Levittown, created economies of scale which have diminished in today’s market, leading to smaller and less productive firms. |
| Patent Activity Drop | Since the 1970s, the construction industry has seen a decline in patent activity, indicating less innovation compared to other sectors. |
| Intergenerational Wealth Transfer | There has been a significant decline in housing wealth for younger generations, exacerbating economic disparity. |
Summary
The housing affordability crisis is a significant issue impacting many Americans today, where homeownership increasingly slips out of reach for an entire demographic. Factors contributing to this crisis include soaring housing prices, stifling land-use regulations, and a notable decline in productivity within the construction industry. As economic growth continues to thrive, the housing sector distinctly lags behind, constrained by policies that favor local interests over efficient development. To address the looming housing crisis effectively, a reevaluation of current land-use regulations and a push for innovative building practices are essential.