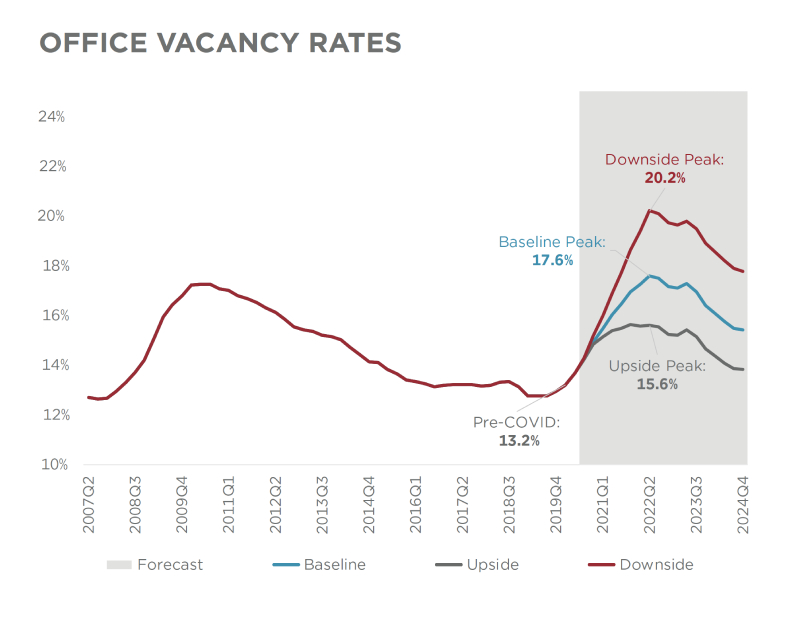
Office vacancy rates have surged dramatically in recent years, raising alarm bells for economists and investors alike. With many businesses embracing hybrid or remote work models, the demand for commercial real estate has plummeted, leading to significant increases in vacancy rates across major urban centers. This shift not only impacts landlords but also poses broader economic questions, as higher vacancy rates can depress property values and affect financial stability, particularly for banks heavily invested in real estate loans. As interest rates remain high, the economic impact of office vacancies may compound, potentially leading to bank losses in the commercial real estate sector. Understanding this complex interplay between office vacancy rates, real estate financing, and economic health is crucial as we navigate the post-pandemic landscape.
The topic of vacant office spaces, often termed as unused commercial properties or underutilized real estate assets, has taken center stage in today’s economic discussions. The pandemic has ushered in a new era where many employees have shifted to flexible working arrangements, leaving office buildings in limbo and contributing to the rise in vacancy rates. This phenomenon is concerning for financial institutions as the repercussions extend beyond empty offices; the potential issues surrounding real estate loans and regional bank stability are significant. Moreover, with the specter of rising interest rates, the economic ramifications of these vacancies could be more profound than initially anticipated. As the market adjusts, stakeholders must pay close attention to the dual challenges of declining occupancy and the impending debt maturities associated with commercial real estate.
The Economic Implications of High Office Vacancy Rates
High office vacancy rates indicate a significant shift in the real estate landscape, reflecting changes in workforce dynamics and corporate policies. As remote and hybrid work models become increasingly normalized, businesses are reconsidering their physical office space needs. Cities like Boston, with vacancy rates ranging from 12% to 23%, show a clear trend that can result in economic stagnation. If businesses scale back their office space, this could lead to diminished demand for services and businesses that thrive in vibrant urban environments, ultimately harming the local economy.
Moreover, long-term implications of high vacancy rates can be detrimental to community development and infrastructure. Declining demand for office space reduces property values, resulting in lower tax revenues for cities. This downturn may limit funding for public services, schools, and infrastructure projects, stifling economic growth and potentially leading to a vicious cycle of decline. The real estate market’s struggles, particularly when coupled with rising interest rates, can also hamper regional economic prospects, highlighting the interconnectivity between office vacancy rates and broader economic health.
Understanding the Economic Impact of Office Vacancies
The economic impact of high office vacancy rates extends beyond just the real estate sector; it influences job markets, local businesses, and investments. Banks that heavily finance commercial real estate could face increased risks if office vacancies remain persistent. With a substantial amount of commercial real estate loans coming due and a notable segment of the market underperforming, banks may experience losses that ripple through the financial system. The result may lead to tightened lending standards, impacting consumers and businesses reliant on credit.
In particular, the health of regional banks is at risk due to their significant exposure to commercial real estate. Should delinquencies on real estate loans spike, it could lead to a banking crisis that exacerbates economic downturns resulting from office vacancies. Therefore, understanding the economic impact of office vacancies is essential—it serves as a barometer for the overall financial health of both local markets and the larger economy.
Commercial Real Estate and the Rising Tide of Bank Losses
As the commercial real estate sector grapples with high vacancy rates, financial institutions must brace for potential bank losses. Experts like Kenneth Rogoff highlight the vulnerability of regional banks that may face significant impairments due to the strain of maturing loans amid less favorable market conditions. When a notable percentage of commercial mortgage debt becomes overdue, banks must reconsider their lending strategies and potentially brace for losses that could stretch their resources, impacting consumer lending.
The relationship between commercial real estate health and bank stability underscores the importance of sound economic policies. As banks navigate these challenges, they may tighten lending practices to safeguard against further exposure to bad loans. This contraction of credit availability can inhibit entrepreneurial activities and growth, reflecting the broader economic ramifications of commercial real estate’s struggles.
Interest Rates and Their Influence on Real Estate Stability
Interest rates play a crucial role in shaping the dynamics of the commercial real estate market. As rates climb, borrowing becomes more expensive, squeezing investors who had initially taken advantage of lower rates to finance property acquisitions. The combination of high office vacancy rates and rising interest rates creates a perfect storm for stakeholders in the real estate market, particularly those with imminent loan maturities. In this context, the unpredictability of interest rate movements becomes a pivotal factor influencing investor confidence and market stability.
Moreover, the reluctance of the Federal Reserve to significantly reduce interest rates adds to the uncertainty. As long-term rates remain elevated, refinancing becomes less feasible for numerous real estate investors, leading to increased market volatility. The specter of rising interest rates will continue to loom over commercial real estate, presaging challenges that could emerge as economic conditions evolve. This ongoing situation marks a critical juncture for real estate investors and financial institutions in maintaining economic stability.
Navigating the Future: Strategies to Mitigate Office Vacancy Challenges
To mitigate the challenges posed by high office vacancy rates, stakeholders might need to adopt innovative strategies for revitalizing their spaces. Conversion of underutilized office buildings into mixed-use complexes or residential properties could present a viable solution to address the housing crisis while simultaneously lifting property values. Such strategies could foster community development and increase foot traffic in urban areas, supporting local businesses impacted by declining office occupancy.
Additionally, urban planning initiatives that promote flexible office spaces and collaborative work environments may appeal to companies looking to return to physical work settings while accommodating the evolving expectations of a hybrid workforce. Implementing such strategies could rejuvenate demand for office spaces, counteracting the negative economic effects of prolonged high vacancy rates.
Consumer Repercussions of the Commercial Real Estate Crisis
The repercussions of the commercial real estate downturn extend far beyond the banks; consumers also face fallout from high office vacancy rates. A reduction in office space demand affects various sectors that service those businesses, from local cafes to cleaning services, ultimately leading to job losses and lower disposable income in affected regions. As businesses scale back or close their operations, the overall economic landscape suffers, impacting consumer confidence and spending.
Moreover, as banks tighten lending practices in response to potential losses tied to commercial real estate loans, consumers may find it more challenging to secure favorable financing. This tighter credit environment could stifle personal economic mobility and hinder growth opportunities. It showcases the complex interplay between commercial real estate and consumer experiences and highlights the far-reaching effects of high office vacancy rates.
The Role of Regulatory Measures in Commercial Real Estate
Regulatory measures will play a vital role in addressing the challenges posed by high office vacancy rates and their economic repercussions. Following the 2008 financial crisis, stricter regulations were implemented for large banks, but many regional banks face less stringent frameworks. As vulnerabilities expose these banks to potential losses, regulatory frameworks may need to evolve, ensuring that lending practices are sufficiently rigorous to safeguard the economy from the pitfalls of over-leveraged investments in commercial real estate.
The effectiveness of regulatory measures in maintaining financial stability within the sector cannot be understated. Introducing smart policies that incentivize conversion of underutilized office spaces while supporting banks in weathering the economic storm may prevent significant regional economic downturns. Industry stakeholders must advocate for insightful regulatory adaptations that consider the evolving needs of the market while promoting sustainable growth.
The Future of Office Space: Trends and Adaptations
The future of office space is bound to transform, influenced heavily by changing work patterns post-pandemic and economic pressures like high vacancy rates. Companies may look to redesign their office spaces to incorporate flexibility and amenities that cater to a hybrid workforce, emphasizing employee well-being and productivity. By adapting to these trends, businesses can enhance their appeal while fostering an environment conducive to collaboration.
The adaptive reuse trend will likely accelerate as cities seek to find solutions to high vacancy rates. By repurposing existing office buildings into mixed-use developments, cities can revitalize urban landscapes, supported by a recovering job market and changing consumer dynamics. This pivot not only addresses the commercial real estate sector’s challenges but also rejuvenates local economies, emphasizing the need for innovation in real estate planning.
Bank Preparedness and the Potential for Economic Fallout
The preparedness of banks to navigate potential shocks stemming from high office vacancy rates and delinquent real estate loans will significantly shape the future economic landscape. While larger banks have diversified portfolios and can absorb some losses, the stability of regional banks hangs in the balance as they deal with concentrated exposure to commercial real estate. This uneven risk profile could amplify the economic fallout if significant delinquencies occur, underscoring the need for diligent risk management and strategic contingency planning within financial institutions.
The interactions between real estate performance and banking stability reflect the interconnectedness of the financial ecosystem. Any potential fallout from the commercial real estate sector could necessitate interventions ranging from regulatory adjustments to governmental support. Such measures would be instrumental in bolstering the banking sector, protecting consumers from subsequent economic tremors, and fostering an environment where a diverse range of commercial projects can thrive.
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors are contributing to high office vacancy rates in commercial real estate?
High office vacancy rates in commercial real estate have resulted from decreased demand following the pandemic, which has led many companies to adopt remote or hybrid work models. Additionally, rising interest rates have made financing more expensive, which further discourages new investments in office properties.
How do office vacancy rates impact the economic stability of cities?
High office vacancy rates can negatively impact the economic stability of cities by depressing property values, reducing tax revenues, and leading to diminished investments in local businesses. In turn, this can diminish overall economic growth and vitality in urban areas.
What are the implications of rising office vacancy rates on bank losses?
Rising office vacancy rates could lead to significant bank losses, particularly for regional banks heavily invested in commercial real estate loans. If property values decline further due to high vacancies, banks may face increased delinquencies on loans secured by these properties, putting their financial health at risk.
What role do interest rates play in the commercial real estate market and office vacancy rates?
Interest rates significantly influence the commercial real estate market. When interest rates rise, financing costs increase, leading to reduced demand for office space. High interest rates can also make refinancing existing loans costly for property owners, further exacerbating office vacancy rates.
How do office vacancy rates relate to the overall health of the commercial real estate sector?
Office vacancy rates serve as a critical indicator of the health of the commercial real estate sector. High vacancy rates often signal a decline in demand for office space, which can lead to falling property values, reduced investments, and potential financial instability within the sector.
What are the potential economic impacts of a surge in delinquent office loans?
A surge in delinquent office loans could have far-reaching economic impacts, including potential bank failures, tighter lending standards, and decreased investment in local economies. Such scenarios could particularly affect regional banks, leading to broader economic instability.
How might high office vacancy rates affect pension funds and investors?
High office vacancy rates can adversely affect pension funds and investors who hold stakes in commercial real estate. As property values decrease, the expected returns on these investments diminish, impacting the financial health of pension funds that rely on stable real estate income.
What strategies can be employed to address high office vacancy rates in urban areas?
To address high office vacancy rates, urban areas can explore strategies like repurposing vacant office spaces for residential use, promoting flexible workspaces, and incentivizing companies to return to office settings through tax breaks or grants, which can stimulate demand for commercial properties.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| High Office Vacancy Rates | Vacancy rates range from 12% to 23% in major U.S. cities, affecting property values. |
| Commercial Mortgage Debt | 20% of $4.7 trillion in commercial mortgage debt is due this year, risking bank liquidity. |
| Impact on Banks | Large banks are better regulated but small and medium banks are at higher risk of failure. |
| Potential Economic Damage | High vacancy rates could lead to decreased consumption and stricter lending from regional banks. |
| Investor Optimism | Some investors believe interest rates will fall, which could improve conditions. |
| Possible Remedies | Lower long-term interest rates may help, but that is unlikely without a recession. |
Summary
Office vacancy rates are presenting significant challenges for the economic landscape, especially as lingering high vacancy rates continue to cast a shadow over commercial real estate. Despite some optimism regarding the future of interest rates and commercial properties, the current environment necessitates careful monitoring and action by financial institutions and investors alike to mitigate potential fallout.